Welcome to Jim Spohrer’s blog site (updated August 2024) for service in the AI era information, which studies responsible entities learning to invest to become “better” future versions of themselves.
Jim’s Bio
(72 words):
Jim Spohrer is a retired industry executive (IBM, Apple) based in the Bay Area California. He serves on the Board of Directors of the non-profit International Society of Service Innovation Professionals (ISSIP) and ServCollab (“Serving Humanity Through Collaboration), and also a UIDP (University-Industry Demonstration Program) Senior Fellow. He has over 90 publications and 9 patents. He has a PhD from Yale in Computer Science/Artificial Intelligence and a BS in Physics form MIT.
(142 words):
Jim Spohrer is a student of service science and open-source, trusted AI. He is a retired industry executive (Apple, IBM), who is a member of the Board of Directors of the non-profit International Society of Service Innovation Professionals (ISSIP). At IBM, he served as Director for Open Source AI/Data, Global University Programs, IBM Almaden Service Research, and CTO IBM Venture Capital Relations Group. At Apple, he achieved Distinguished Engineer Scientist Technologist (DEST) for authoring and learning platforms. After MIT (BS/Physics), he developed speech recognition systems at Verbex (Exxon), then Yale (PhD/Computer Science AI). With over ninety publications and nine patents, awards include AMA ServSIG Christopher Lovelock Career Contributions to the Service Discipline, Evert Gummesson Service Research, Vargo-Lusch Service-Dominant Logic, Daniel Berg Service Systems, and PICMET Fellow for advancing service science. In 2021, Jim was appointed a UIDP Senior Fellow (University-Industry Demonstration Partnership).
One slide version of bio:
Picture (2022, Santa Clara, CA – ISSIP Event):
Picture (2008, San Jose, CA, while Director, IBM Almaden Service Research Group):
Picture (October 15, 2016 Chongqing China, while keynoting at 9th ICSS -International Conference on Service Science):

Jim Spohrer (Oct 2016)

Jim Spohrer (Feb 2018) – photo by Michael Maximillien
In 2011 during IBM’s Centennial Celebration, Jim Spohrer was recognized as an IBM Innovation Champion for his contributions to service science. Service science is one of the 100 innovations celebrated during IBM’s Centennial as an IBM Icon of Progress: http://www.ibm.com/ibm/history/ibm100/us/en/icons/servicescience/.
Service is defined as the application of knowledge for mutual benefits, a type of value co-creation from win-win interactions. It is the observable and measurable phenomena of responsible entities applying knowledge to achieve non-zero-sum outcomes from interactions and change. Service is a fundamental concept that connects is surprising ways to other fundamental concepts (areas of study) where entities are part of an evolving ecology with auto-catalytic properties: Atoms and stars (physics), molecules and planets (chemistry), organisms and niches (biology), humans and cultures (social sciences), with many other transdisciplinary connections to nations and law (politics), businesses and risk (organization theory), value and resources, supply and demand, comparative advantage (economics), physical symbol systems and algorithms (computer science), processes and optimization (operations research), signals and feedback loops (control theory), structure-function-and-behavior and emergence (systems), history and predictions (data science), contracts and evidence (law), entropy and communications (information theory), environment and evolution (ecology), decision-making (management), and many other areas.
The service ecology (all the people, businesses, and nations) is evolving new types of service (AKA win-win games, value co-creation work and production processes), and (eventually, est. 2045) their trust-enhancing, AI-based “digital twins” may do so as well.
How is service science different from data science (which fuels artificial intelligence)?
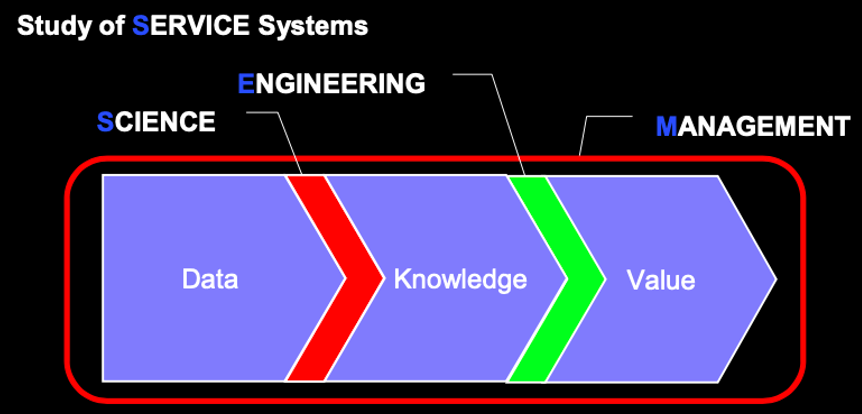
Service science is the study of service systems (people, businesses, nations – their capabilities, constraints, rights, responsibilities, interactions, and outcomes). Service is defined as the application of knowledge for mutual benefits (AKA value co-creation, or win-win games). Service system entities (people, businesses, nations) are some key types of responsible entities that generate data, lots and lots of data! Data science deals with the data that service system entities generate. Data science is an interdisciplinary field that uses scientific methods to extract knowledge and insights from data to apply in many domains. Service science studies the transformation and innovation of service systems, responsible entities which generate mountains of data and are constantly changing! Service systems (people, businesses, nations) generate data about activities, interactions and outcomes. Importantly, all the many types of service systems can also be viewed as responsible entities learning to invest in change. All responsible entities invest to become better future versions of themselves, more successful people, businesses, nations. All responsible entities, that can learn to apply knowledge for mutual benefits (provision service), can also learn to learn to invest better in their future success, by recognizing the more valuable activities and interactions (optimization, social learning, and invention) that lead to more valuable outcomes, and thereby more resources for future resource integration and investment opportunities. Data science can be viewed as one type of activity that is part of service science that is used for accelerated improvement of service systems across industries, finance, retail, healthcare, etc. Learning to invest more mindfully and systematically is what responsible entities do as they coordinate their upskilling (co-elevation of capabilities) for the future. As entities upskill (become more capable) themselves, they can innovate better and seize more opportunities to interact and co-create value; they can invent better and better win-win games to play. The innovation of service systems (service innovation), is not just about better technology, but about an evolving ecology of responsible entities interacting with better natural and technological infrastructure, better business models and government institutions, better trust and sharing of information, better human-centered design and skills in individuals. Service innovations lead generally to better quality-of-life and opportunities for entities, and specifically to better non-zero-sum interactions among the entities in business and society. Better non-zero-sum interactions has been described as the logic of human destiny. The history of humankind provides clear lessons of upward interaction spirals (increased understanding of ourselves and others) and downward interaction spirals (increased fear of the future and others). AI will allow us to build better “digital twins” of all entities, ourselves and others, increasing our understanding and improving our interactions and outcomes. Service science like data science, is one of the sciences of “better.” While service science has a focus on systems, which are responsible entities learning to invest in co-creating better future versions of themselves (service systems innovation), instead data science focuses on datasets coming from parts of service systems, and then extracting knowledge and insights that can be applied in different domains. From a service science perspective, a key purpose for data science is to produce better AI systems which can act as digital twins for all service systems. Complexity economics can then make use of these digital twins for all service systems to perform trillions of simulations of the evolving ecology of entities and their possible strategies. From a service science perspective, a key purpose of complexity economics is simulate possible entity interaction strategies and thereby search for improved government institutions and public policy strategies, business model strategies, individual upskilling strategies, and improve the way responsible entities learn to invest in creating better future versions of themselves and their AI digital twins. Service science is based on the worldview of Service-Dominant Logic. Service science is an emerging transdiscipline that seeks to integrate better all existing disciplines into an integrated whole, requiring T-shaped skills (depth and breadth) in people, and builds on the conceptual foundation of multidisciplinary thinking, including the “accelerating socio-technical system design loop” and “techno-extension factors” that augment human intelligence, to address complex, urgent problems.
Service science is short for SSME+DAPP = Service Science Management Engineering (tool system) + Design Arts Pubic Policy (human system).
Dossier Resume Curriculum Vitae Dec 2020 at IBM

The best way to predict the future is to inspire the next generation of students to build it better
Contact:
Dr. James (“Jim”) C. Spohrer
Innovation Champion (http://www-03.ibm.com/ibm/history/ibm100/us/en/icons/servicescience/)
ISSIP (http://www.issip.org)
Contact:
Address: ISSIP, #431, 3561 Homestead Road, Santa Clara, CA 95051-5161
spohrer@gmail.com 408-829-3112 (iPhone)
Skype: james.clinton.spohrer
Social Media Me:
LinkedIn: Jim Spohrer (http://www.linkedin.com/in/spohrer/)
Twitter: @JimSpohrer (https://twitter.com/JimSpohrer)
Bio: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jim_Spohrer
Blog: http://www.service-science.info
Slides: http://www.slideshare.net/spohrer
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCkFGgjwrcJyXbPoaTjeMcvw
GitHub: https://github.com/jimspohrer
Patents and Publications
http://scholar.google.com/citations?user=7T2Pz1YAAAAJ
June 2021 (h-index all = 49, meaning that 49 of my publications have been cited 49 times or more)



Pingback: Engelbart on Improving Improvement – Collective IQ Review
Pingback: Mycroft Cognitive Mediator: Enhancing Team Science – Service Science
Pingback: Why Engineers Need To Develop T-Shaped Skills | Product Lifecycle Report
Pingback: Why Engineers Need Develop to T-Shaped Skills | PTC
Pingback: Why Engineers Need Develop T-Shaped Skills | PTC
Pingback: Social Physics: Selected Quotes | Service Science
Pingback: WT InfoTech
Pingback: Competing for Collaborators | Service Science
Pingback: The Well-Read Service Scientist
Pingback: Learning Collaboration from the NFL's Anti-fragility - Forbes
Pingback: HSSE-2014 Session: The Education of Service Innovators « Service Science
KPIs for cities and universities are changing….
As more emphasis gets put on university KPIs related to entrepreneurship and new job creation, the focus on university knowledge transfer (teaching) KPIs will orient towards cities — cities will increasingly provide access to educational resources for their citizens, for urban life-long learners…. this will be a city KPI… how well they help their citizens stay current on skills for local businesses…
The reason this is important is because the high unemployment rates in the future will have a significant percentage (around 33% unfilled) due to a skills gap in the regional workforce:
Why Jobs Remain Unfilled Even Though Unemployment is High [INFOGRAPHIC]
http://mashable.com/2012/09/10/job-openings-unemployment/
We have to Mind The (Skills)Gap better as a society…
http://blogs.hbr.org/cs/2012/09/mind_the_skills_gap.html
We have to never stop learning…
http://www.nytimes.com/2012/09/22/business/to-stay-relevant-in-a-career-workers-train-nonstop.html?pagewanted=all&_moc.semityn.www
The best way to predict the future is to inspire the next generation of university students to build it better
http://www.slideshare.net/spohrer/smarter-planet-asee-glf-20120920-v2